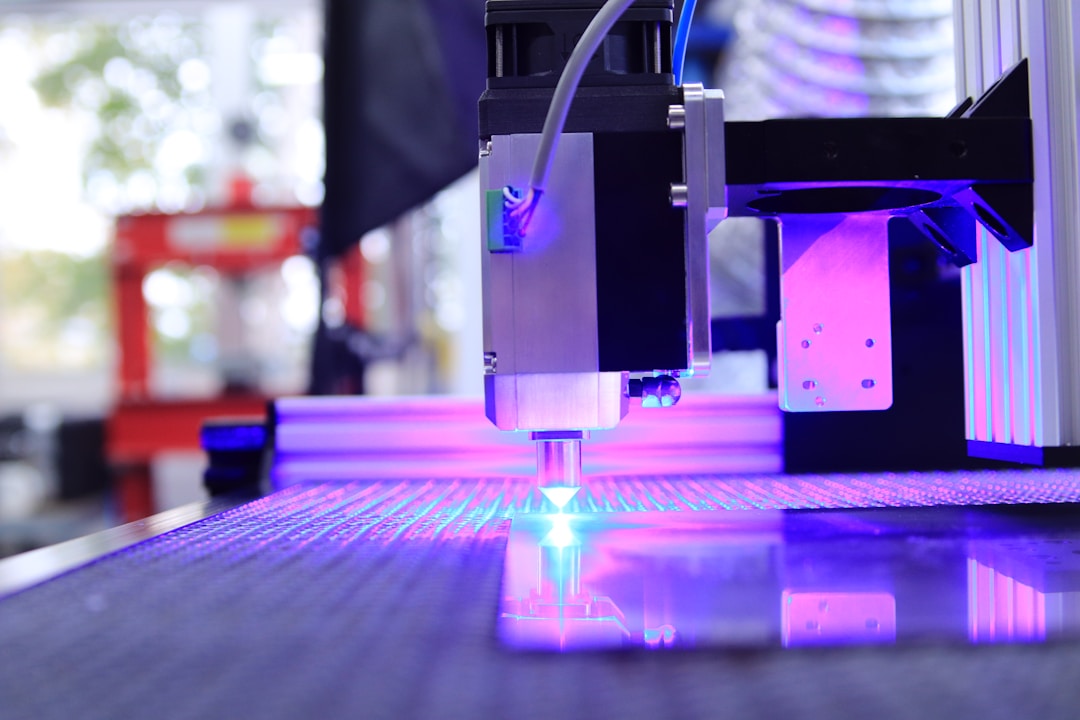
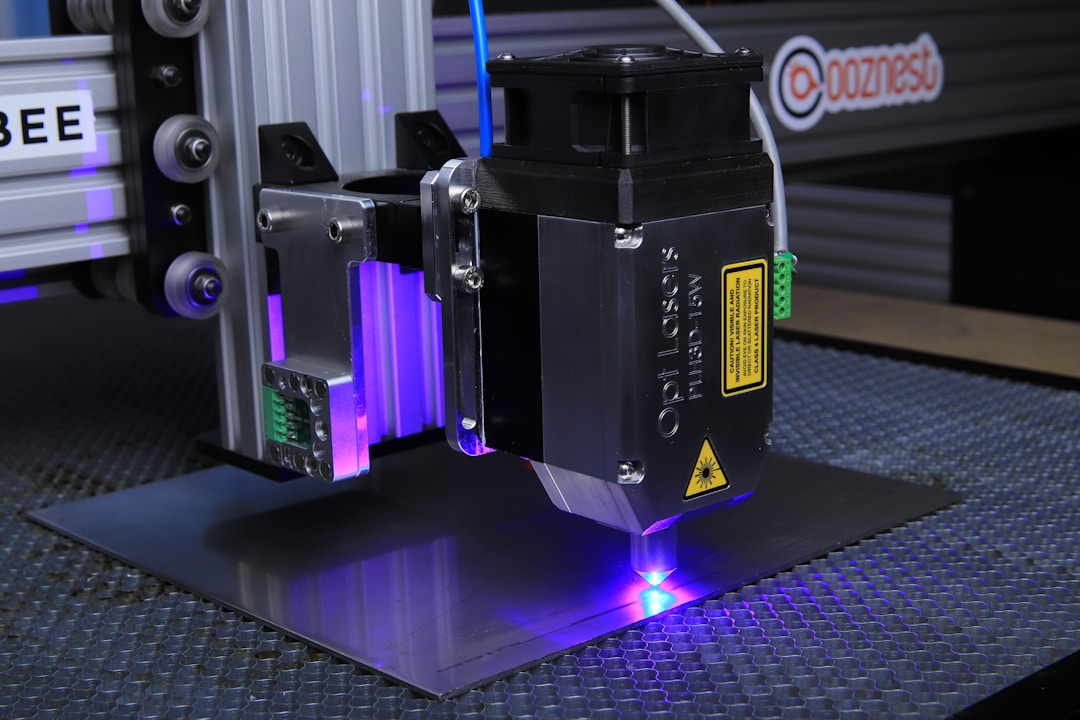
Technology empowers innovation and tax incentives help the laser industry grow and strengthen
Laser technology, known as the "fastest knife," "most accurate ruler," and "brightest light," is an important scientific and technological innovation that emerged after nuclear energy, computers, and semiconductors. Recently, the 2024 World Laser Industry Conference was successfully held in Jinan. The reporter learned that there are currently over 300 laser enterprises in the city, and the export scale of laser equipment products mainly focused on laser cutting ranks first in the country. Jinan has become the largest and important laser equipment industry base in northern China.
Apr 02,2024
The world's strongest laser has been activated so far
The world's most powerful laser has recently been activated. On March 31st, the Physicist Organization Network reported that the system can enable laser pulses to reach a peak of 10 terawatts (1 terawatt=100 terawatts=1015 watts) within 1 femtosecond (1000 trillions of a second), which is expected to promote revolutionary progress in multiple fields from medicine to basic physics and space.
Apr 02,2024
Laser nanomanufacturing technology
Micro manufacturing technology is a cutting-edge and interdisciplinary field that gradually developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Its rapid development will bring about a revolutionary change in almost all industrial sectors in the 21st century. The widespread application of micro manufactured products will trigger a new technological revolution, just like the impact of microelectronics technology on the world. This is a high-tech challenge and opportunity, which may become a breakthrough for China to catch up with the world's advanced level and leap towards high-tech. Nanotechnology and laser processing technology are the core of micro manufacturing technology.
Apr 02,2024
Comprehensive Analysis of Nanolaser Technology and Its Applications
The development of nanotechnology has made the combination of microelectronics and optoelectronics closer, greatly improving the performance of optoelectronic devices in areas such as information transmission, storage, processing, computation, and display. Applying nanotechnology to existing radar information processing can increase its capabilities by 10 to several hundred times, and even ultra-high resolution nanoaperture radar can be placed on satellites for high-precision ground reconnaissance. Recently, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology fed excited barium atoms into lasers one by one, emitting a useful photon from each atom with astonishing efficiency.
Jul 28,2022
Detailed explanation and latest progress of laser surface nanomaterialization technology
After the successful development of high-power lasers in the 1970s, laser surface treatment technology entered practical applications and rapidly developed, including laser quenching (laser phase change hardening surface modification technology), laser remelting, and laser surface alloying
Jan 10,2022
The application of ultra-thin homogenizing plate in highly integrated ultra-light electronic devices
Since 2019, with the emergence and rapid development of the fifth generation mobile communication technology (5G technology), electronic products, especially smartphones, tablets, and other products, have been increasingly moving towards high performance, high integration, and miniaturization. To meet the performance and size requirements of products, the transistor density on electronic chips is increasing.
Nov 12,2021
The research status and development trend of ultra-thin uniformly heated plates
With the emergence and rapid development of the fifth generation mobile communication technology (5G technology), electronic products, especially smartphones, tablets, and other products, are increasingly moving towards high-performance, high integration, and miniaturization. The exponential increase in power consumption will lead to electronic chips generating excessively high heat flux density and operating temperature in narrow spaces, further causing severe thermal runaway problems. Ultra thin uniform heat plates have excellent thermal conductivity, large heat transfer area, good temperature uniformity, and high reliability, making them the primary way to solve the heat dissipation problem of electronic equipment. In order to meet the cooling needs of modern miniaturized electronic devices in the 5G era, further ultra-thin homogenization plates are currently a research hotspot in the industry and academia. Based on this, an overview of the heat transfer principle of ultra-thin homogenization plates is provided, with a focus on summarizing the current research status of ultra-thin homogenization plate structure design at home and abroad, including gas-liquid channel layout structure and liquid absorption core structure. The current packaging and manufacturing process of ultra-thin homogenization plates is introduced, and the problems in achieving extreme ultra-thinness are analyzed. Finally, the research trend and development prospects of ultra-thin homogenization plates in the field of heat dissipation such as highly integrated ultra-light electronic devices are scientifically predicted.
Nov 12,2021
Direct femtosecond laser surface nanostructures/microstructures and their applications
Surface morphology is a key factor in controlling the optical, mechanical, wetting, chemical, biological, and other properties of solid surfaces. In recent years, femtosecond laser surface nanostructures have become a new and multifunctional technology used to produce various nanostructured materials, suitable for wide applications in photonics, plasma electronics, optoelectronics, biochemical sensing, micro/nanofluidics, optofluidics, biomedical and other fields. In the past decade, this technology has received a lot of research attention due to the following advantages: (1) it can process almost all types of materials, including metals, semiconductors, glass, and polymers; (2) Non planar machining capability; (3) Capable of generating nanostructures in the surface region from microscale to macroscopic scale; (4) Under normal environmental conditions, maskless single-step high-speed processing is required without the need for a clean room environment.
Nov 12,2021








 Language
Language